iqtoolkit-analyzer
← Back to Index
🔬 Remote Ollama Testing Guide
This guide shows you how to test IQToolkit Analyzer against a remote Ollama server for distributed deployment scenarios.
🎯 Overview
You can run Ollama on a dedicated server (e.g., a GPU-equipped machine) and connect to it from your development or analysis machines. This is ideal for:
- Centralized AI infrastructure: One powerful GPU server serving multiple analysts
- Development/production separation: Dev machines connect to staging/prod Ollama servers
- Privacy-compliant deployments: Keep AI processing within your network perimeter
- Resource optimization: Share expensive GPU resources across teams
🖥️ Server Setup
1. Install Ollama on Your Server
# SSH to your server (e.g., 192.168.0.30)
ssh user@192.168.0.30
# Install Ollama
curl -LsSf https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
# Start Ollama service
ollama serve
# Pull the SQL-specialized model
ollama pull a-kore/Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B
2. Verify Server is Running
# Check if Ollama is listening
curl http://localhost:11434/api/version
# List available models
ollama list
3. Configure Firewall (if needed)
Ensure port 11434 is accessible from your client machines:
# Example for Ubuntu/Debian with ufw
sudo ufw allow 11434/tcp
# Example for firewalld (CentOS/RHEL)
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=11434/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
💻 Client Setup
1. Install Dependencies
# On your local machine
cd /path/to/iqtoolkit-analyzer
# Create/Select a Poetry environment (Python 3.13 recommended)
poetry env use python3.13
# Install dependencies
poetry install --with dev,test
2. Test Connection
# Set the remote Ollama host
export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434
# Quick connection test
poetry run python -c "import ollama; print(ollama.list())"
Expected output:
models=[Model(model='a-kore/Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B:latest', ...)]
🧪 Running Integration Tests
Using the Test Script
The repository includes a comprehensive test script that validates the remote connection:
# Run the integration test
export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434
python test_remote_ollama.py
Expected output:
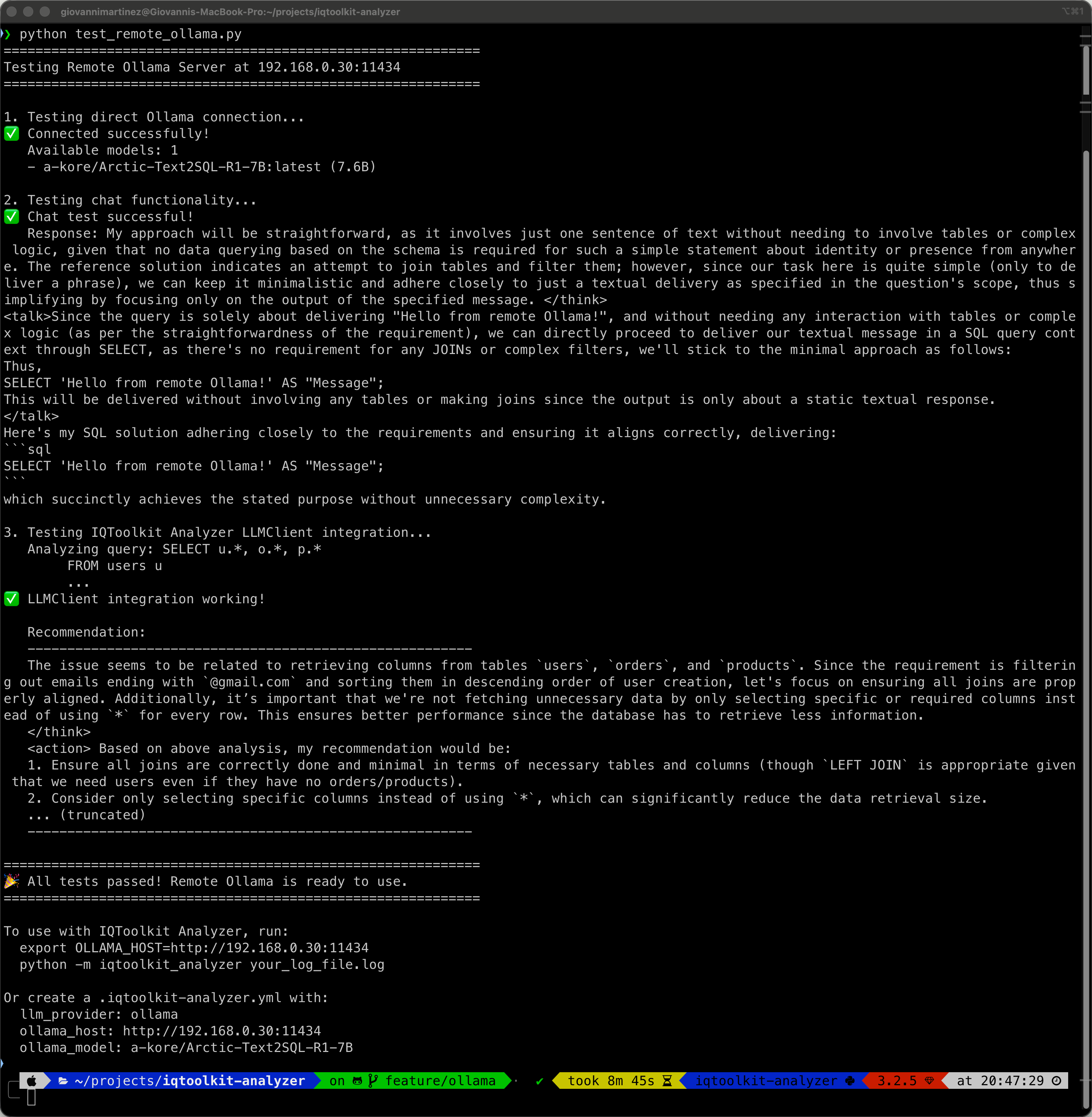
The test script validates:
- ✅ Direct connection to remote Ollama server
- ✅ Model availability and version information
- ✅ Chat functionality with the SQL-specialized model
- ✅ Full IQToolkit Analyzer LLMClient integration
- ✅ AI-generated query optimization recommendations
Running Unit Tests
Use the provided pytest configuration to run tests without coverage (for faster testing):
# Run all LLM client tests
OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434 pytest -c pytest-remote.ini tests/test_llm_client.py -v
# Run only Ollama-specific tests
OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434 pytest -c pytest-remote.ini tests/test_llm_client.py::TestLLMClientOllama -v
# Run a specific test
OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434 pytest -c pytest-remote.ini \
tests/test_llm_client.py::TestLLMClientOllama::test_ollama_custom_host -v
Example output:
tests/test_llm_client.py::TestLLMClientOllama::test_ollama_initialization PASSED
tests/test_llm_client.py::TestLLMClientOllama::test_ollama_generate_recommendations PASSED
tests/test_llm_client.py::TestLLMClientOllama::test_ollama_custom_host PASSED
⚙️ Configuration
Option 1: Environment Variable (Temporary)
# Set for current session
export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434
# Run analysis
python -m iqtoolkit_analyzer your_log_file.log
Option 2: Configuration File (Persistent)
Create or edit .iqtoolkit-analyzer.yml:
# AI Provider Configuration
llm_provider: ollama
ollama_model: a-kore/Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B
ollama_host: http://192.168.0.30:11434
# LLM Settings
llm_temperature: 0.3
max_tokens: 300
llm_timeout: 30
# Analysis Options
top_n: 10
min_duration: 1000
output: reports/analysis.md
Then run without environment variables:
python -m iqtoolkit_analyzer your_log_file.log
Option 3: Shell Profile (Permanent)
Add to your ~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc, or ~/.profile:
# Remote Ollama Configuration
export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434
Reload your shell:
source ~/.bashrc # or ~/.zshrc
🔍 Analyzing PostgreSQL Logs
With the remote server configured, analyze logs normally:
# Basic analysis
python -m iqtoolkit_analyzer postgresql /path/to/postgresql.log --output report.md
# Advanced analysis
python -m iqtoolkit_analyzer postgresql /path/to/postgresql.log \
--output report.md \
--top-n 15 \
--min-duration 500 \
--max-tokens 200 \
--verbose
The AI recommendations will be generated using the remote Ollama server.
🐛 Troubleshooting
Connection Refused
# Test if server is reachable
ping 192.168.0.30
# Test if port is open
nc -zv 192.168.0.30 11434
# or
telnet 192.168.0.30 11434
Solution: Check firewall rules on the server.
Model Not Found
# List models on remote server
curl http://192.168.0.30:11434/api/tags
# Pull the model on the server
ssh user@192.168.0.30
ollama pull a-kore/Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B
Timeout Errors
Increase timeout in .iqtoolkit-analyzer.yml:
llm_timeout: 60 # Increase from default 30 seconds
Or check network latency:
ping -c 10 192.168.0.30
SSL/TLS Errors
If using HTTPS, ensure valid certificates:
ollama_host: https://192.168.0.30:11434 # Use https://
📊 Performance Considerations
Network Latency
- Local Ollama: <1ms latency
- LAN (same subnet): 1-5ms latency (minimal impact)
- WAN/VPN: 20-100ms+ latency (may affect interactive use)
Recommendation: For best performance, deploy Ollama on the same network segment as your analysis machines.
Bandwidth Requirements
- Model loading: One-time per model (7-8GB for Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B)
- Inference: ~10-50KB per query analysis
- Concurrent users: Server can handle multiple clients simultaneously
Server Resources
- Minimum: 16GB RAM, 4 CPU cores
- Recommended: 32GB+ RAM, 8+ CPU cores, GPU (NVIDIA)
- Storage: 50GB+ for models and cache
🔒 Security Best Practices
Network Security
- Use private networks: Keep Ollama on internal networks only
- VPN access: Require VPN for remote access
- Firewall rules: Restrict port 11434 to authorized IPs only
Authentication (Optional)
For production deployments, consider:
- Reverse proxy with authentication (nginx, Apache)
- API gateway with token-based auth
- Network segmentation and access controls
Data Privacy
- Advantage: All query data stays within your infrastructure
- No external APIs: Data never leaves your network
- Compliance-ready: Meets data residency requirements
📚 Related Documentation
- Ollama Local Setup - Local installation guide
- 5-Minute Ollama Setup - Quick start guide
- Configuration Guide - Complete configuration options
- Getting Started - General usage guide
💡 Tips & Tricks
Multiple Environments
Manage different environments with shell aliases:
# Add to ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc
alias ollama-dev='export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.30:11434'
alias ollama-staging='export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.31:11434'
alias ollama-prod='export OLLAMA_HOST=http://192.168.0.32:11434'
alias ollama-local='export OLLAMA_HOST=http://localhost:11434'
Usage:
ollama-dev
python -m iqtoolkit_analyzer your_log.log
Health Check Script
Create a health check script (check_ollama.sh):
#!/bin/bash
OLLAMA_HOST=${OLLAMA_HOST:-http://localhost:11434}
echo "Checking Ollama at $OLLAMA_HOST..."
curl -s $OLLAMA_HOST/api/version && echo "✅ Server is healthy" || echo "❌ Server is down"
Make it executable and run:
chmod +x check_ollama.sh
./check_ollama.sh
Monitoring
Monitor Ollama server performance:
# On the server
htop # CPU/Memory usage
nvidia-smi # GPU usage (if applicable)
journalctl -u ollama -f # Service logs
Made with ❤️ for distributed AI-powered database analysis